
Extracellular Fluid (ECF) - all fluids found. The intracellular fluid is the fluid contained within cells. These pumps transport ions against their concentration gradients to maintain the cytosol fluid composition of the ions. Intracellular Fluid (ICF) - fluid found in the cells (cytoplasm, nucleoplasm) comprises 60 of all body fluids.
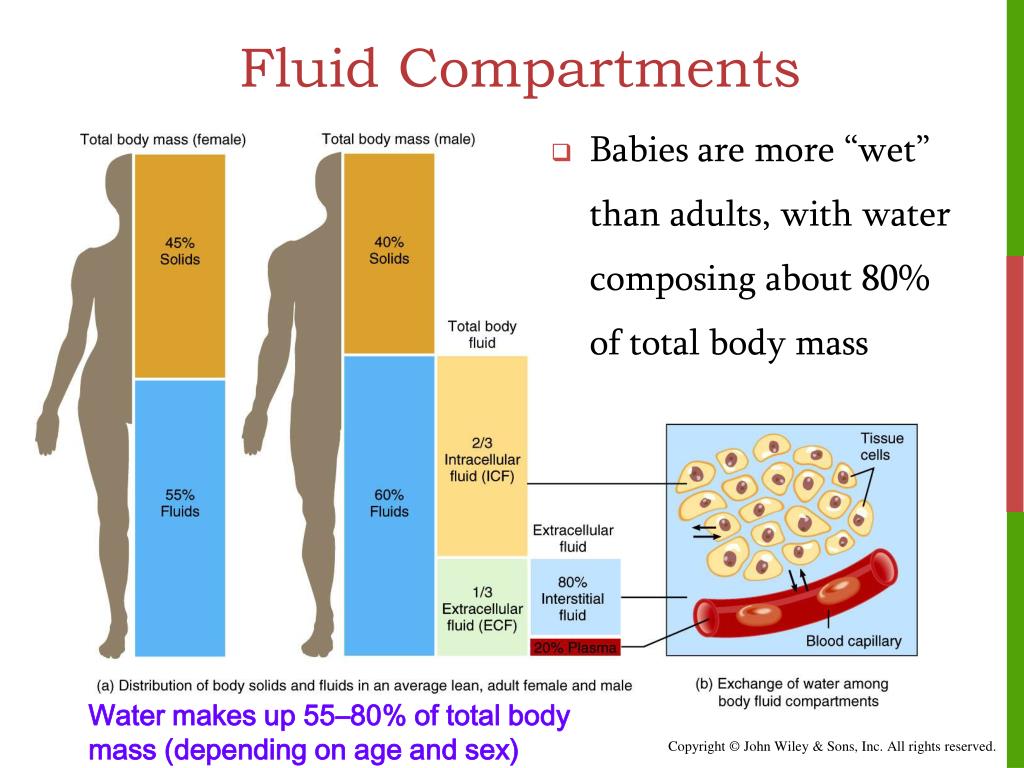
However, it should be noted that due to the differences between differentiated cell types and their functions, the fluid composition of the intracellular fluid is highly variable. The reason for these specific sodium and potassium ion concentrations are Na+/K ATPase pumps that facilitate the active transport of these ions. The concentrations given in Figure 3 represent plasma water and the intracellular fluid of myocytes as illustrative examples. In fact, intracellular fluid accounts for 60 of the volume of body fluids and 40 of a persons total body weight Extracellular fluids (ECF) are fluids found. In contrast to extracellular fluid, cytosol has a high concentration of potassium ions and a low concentration of sodium ions. The cytosol also contains much higher amounts of charged macromolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, than the outside of the cell. The concentrations of the other ions in cytosol or intracellular fluid are quite different from those in extracellular fluid. Abstract The purpose of this study was to test the validity of a multiple frequency bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) technique that estimates extracellular fluid volume (ECV), intracellular fluid volume (ICV), and total body water (TBW). The cell membrane separates cytosol from extracellular fluid, but can pass through the membrane via specialized channels and pumps during passive and active transport. Extracellular fluid (ECF) surrounds the cells serves as a circulating reservoir. The pH of the intracellular fluid is 7.4. Interstitial fluid consists of a water solvent containing sugars, salts, fatty acids, amino acids, coenzymes, hormones, neurotransmitters, white blood cells and. Intracellular fluid (ICF) is the cytosol within the cell. Most of the cytosol is water, which makes up about 70% of the total volume of a typical cell. These enzymes are involved in the biochemical processes that sustain cells and activate or deactivate toxins. This mixture of small molecules is extraordinarily complex, as the variety of enzymes that are involved in cellular metabolism is immense.

The cytosol or intracellular fluid consists mostly of water, dissolved ions, small molecules, and large, water-soluble molecules (such as proteins). Extracellular fluid has two primary constituents: the fluid component of the blood (called plasma) and the interstitial fluid (IF) that surrounds all cells not.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
